Event Driven Microservices: Spring Boot + Kubernetes + Docker + Helm + Google Cloud
This tutorial is just a guide on how to deploy and run microservices reference example by Kenny Bastani, which demonstrates the basics of Event Driven Microservices Architecture using Spring Boot, Spring Cloud, Kubernetes, Docker, Helm and Google Cloud stacks.
Microservices on Google Cloud using SpringBoot, Kubernetes, Docker, Helm
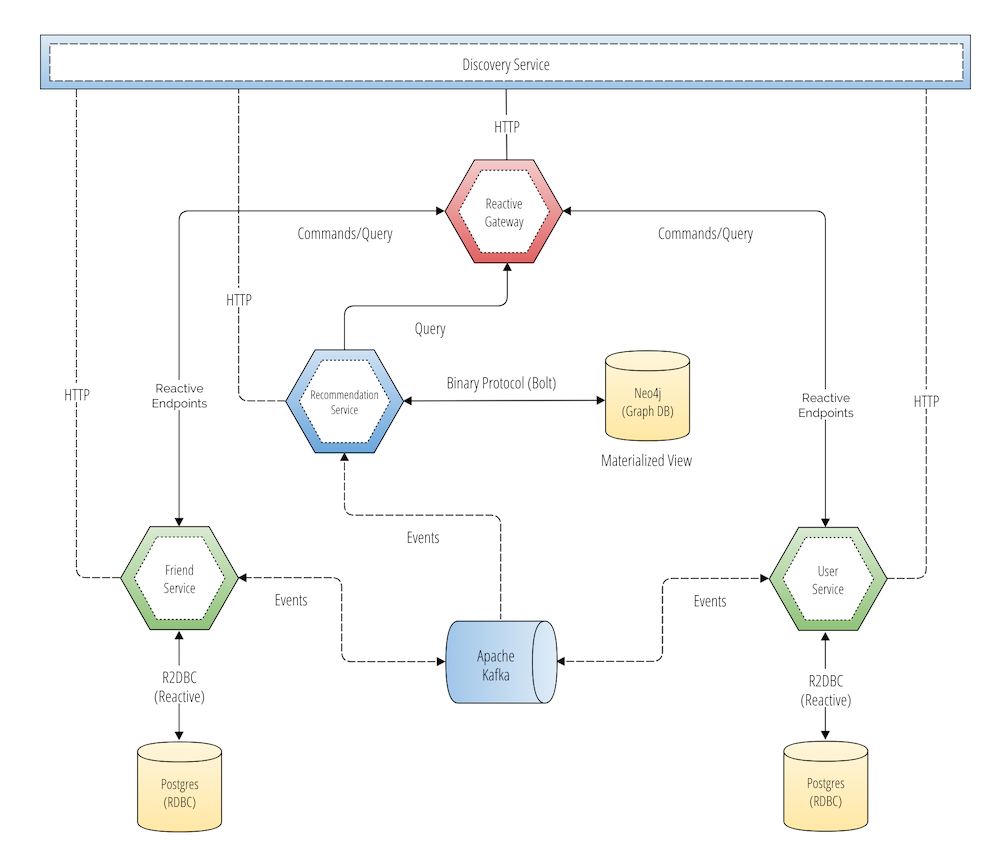
This example built was a social network using vent driven microservices architecture. You can refer for more details on the architecture here.
Picture: GitHub kbastani Event Sourcing Microservices Example
The scope of this tutorial is deployment and running of the above microservices example using helm on Google Cloud Platform i.e., Hyperscale Evaluation as mentioned in the tutorial.
Hyperscale Evaluation
This deployment guide is for users who wanted to run this social network example as a hyper-scalable distributed system with a production Kubernetes cluster that is deployed to a public cloud provider like Google Cloud GKE Cluster. You are going to use Helm as a package manager for Kubernetes that can be used to deploy and manage a scale-out distributed system.
Pre-Requisites
Before you start, make sure you have performed the following tasks:
- Ensure that you have enabled the Google Kubernetes Engine API.
- Ensure that you have installed the Cloud SDK.
- Install Helm by following the instructions https://docs.helm.sh/using_helm/#installing-helm.
Deploy and Run Event Driven Microservices on Google Cloud
1. Create Kubernetes Cluster
To create kubernetes cluster
- Go to Kubernetes Engine -> Clusters -> Create Clusters
- Choose Standard Cluster template and mention name (social-network-cluster) of the cluster. Customize the template if needed otherwise you can leave the defaults for the fields Location type, Zone, Region, node pool etc.,
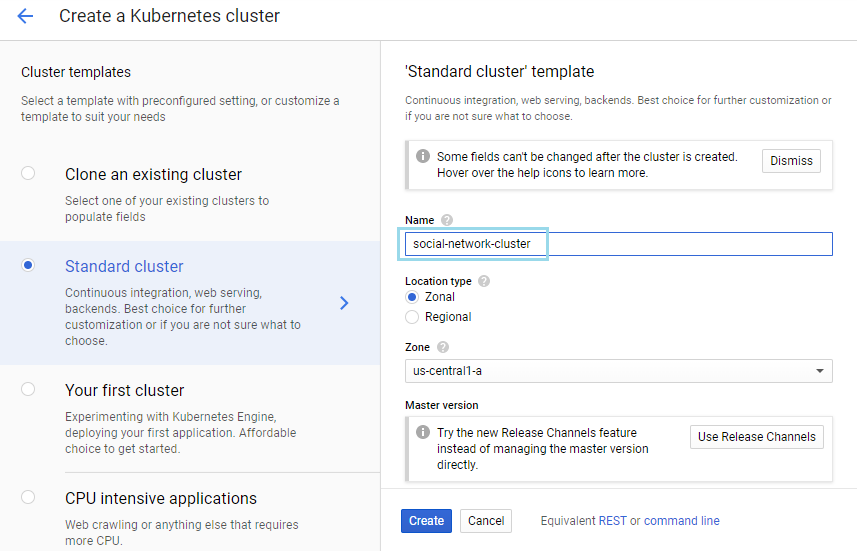
- Click Create
2. Connect to the cluster via command line
You can connect to the cluster via command line or using a dashboard. To configure kubectl command line access you need to run the following command.
$ gcloud container clusters get-credentials social-network-cluster --zone us-central1-a --project sneppets-gcp Fetching cluster endpoint and auth data. kubeconfig entry generated for social-network-cluster.
Then you need to check and ensure you have access to the kubernetes cluster by running the following command
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION gke-social-network-clust-default-pool-2fb1d5e6-750v Ready <none> 7m5s v1.14.10-gke.17 gke-social-network-clust-default-pool-2fb1d5e6-k2x8 Ready <none> 7m5s v1.14.10-gke.17 gke-social-network-clust-default-pool-2fb1d5e6-m6b6 Ready <none> 7m6s v1.14.10-gke.17
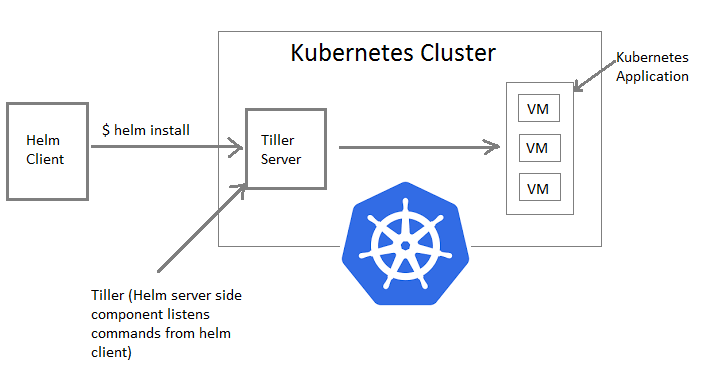
3. Install Helm Tiller (RBAC)
You need to run the following commands to install Tiller (the Helm Server side component) and setup RBAC in to your kubernetes cluster.
$ helm init $HELM_HOME has been configured at /home/nithip2016/.helm. Tiller (the Helm server-side component) has been installed into your Kubernetes Cluster. Please note: by default, Tiller is deployed with an insecure 'allow unauthenticated users' policy. To prevent this, run `helm init` with the --tiller-tls-verify flag. For more information on securing your installation see: https://docs.helm.sh/using_helm/#securing-your-helm-installation
$ kubectl --namespace kube-system create serviceaccount tiller from server (AlreadyExists): serviceaccounts "tiller" already exists
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule \ --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/tiller-cluster-rule created
$ kubectl --namespace kube-system patch deploy tiller-deploy \
-p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"serviceAccount":"tiller"}}}}'
deployment.extensions/tiller-deploy patched
$ helm repo update
4. Clone the git code locally
Clone the Event driven social network microservices code from git to your local.
$ git clone https://github.com/kbastani/event-sourcing-microservices-example.git $ cd event-sourcing-microservices-example
$ ls deployment docker-compose.yml edge-service LICENSE README.md user-service discovery-service Dockerfile friend-service pom.xml recommendation-service
5. Add bitnami helm repo
Add the bitnami helm repository which contains the kafka and zookeeper charts.
$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com "bitnami" has been added to your repositories $ helm repo add incubator https://kubernetes-charts-incubator.storage.googleapis.com "incubator" has been added to your repositories
6. Update dependent charts
You need to run a few helm commands to ensure all dependent charts are available.
$ helm dep update deployment/helm/social-network $ helm dep update deployment/helm/friend-service $ helm dep update deployment/helm/user-service $ helm dep update deployment/helm/recommendation-service
7. Deploy microservices using Helm
Using the above commands/steps Helm and Kubernetes Cluster is all setup. Now its time to deploy the distributed system to kubernetes cluster using the following helm command.
$ helm install --namespace social-network --name social-network --set fullNameOverride=social-network deployment/helm/social-network
Response: NAME: social-network LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Feb 25 12:23:33 2020 NAMESPACE: social-network STATUS: DEPLOYED RESOURCES: ==> v1/ClusterRole NAME AGE social-network-grafana-clusterrole 5s ==> v1/ClusterRoleBinding NAME AGE social-network-grafana-clusterrolebinding 5s ---------------------- ---------------------- ---------------------- ==> v1/Pod(related) NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE edge-service-7659dbb6f8-4jvjd 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 5s friend-db-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s friend-service-559bdfbb99-7f65d 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 5s kafka-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s recommendation-service-6877bbfc4b-p5nmz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s social-network-grafana-96dbbf87-rwjjv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s social-network-neo4j-core-0 0/1 Pending 0 3s social-network-prometheus-kube-state-metrics-86c8c74d9-sxbbm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s social-network-prometheus-node-exporter-4v49v 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 5s social-network-prometheus-node-exporter-lbgrp 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s social-network-prometheus-node-exporter-z78ld 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s social-network-prometheus-server-b8d9d948c-gd456 0/2 Init:0/1 0 4s social-network-zookeeper-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s user-db-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s user-service-8988d7db4-kdlgx 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s --------------------- --------------------- ==> v1/Service NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE edge-service ClusterIP 10.0.5.218 <none> 9000/TCP 5s friend-db ClusterIP 10.0.6.31 <none> 5432/TCP 5s friend-db-headless ClusterIP None <none> 5432/TCP 5s friend-service ClusterIP 10.0.13.135 <none> 8100/TCP 5s kafka ClusterIP 10.0.6.234 <none> 9092/TCP 5s kafka-headless ClusterIP None <none> 9092/TCP 5s recommendation-service ClusterIP 10.0.15.120 <none> 8110/TCP 5s social-network-grafana ClusterIP 10.0.6.73 <none> 80/TCP 5s social-network-neo4j ClusterIP None <none> 7474/TCP 5s social-network-prometheus-kube-state-metrics ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 5s social-network-prometheus-node-exporter ClusterIP None <none> 9100/TCP 5s social-network-prometheus-server ClusterIP 10.0.8.62 <none> 80/TCP 5s social-network-zookeeper ClusterIP 10.0.8.101 <none> 2181/TCP 5s social-network-zookeeper-headless ClusterIP None <none> 2181/TCP,3888/TCP,2888/TCP 5s user-db ClusterIP 10.0.10.203 <none> 5432/TCP 5s user-db-headless ClusterIP None <none> 5432/TCP 5s user-service ClusterIP 10.0.5.130 <none> 8120/TCP 5s ---------------------- ---------------------- ==> v1beta2/Deployment NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE friend-service 0/1 1 0 5s recommendation-service 0/1 1 0 4s social-network-grafana 0/1 1 0 5s user-service 0/1 1 0 4s ==> v1beta2/StatefulSet NAME READY AGE friend-db 0/1 4s social-network-neo4j-core 0/1 3s user-db 0/1 3s
Check the status of deployment and the state of the kubernetes cluster use the following command.
$ kubectl get pods -n social-network Response: -------------- NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE edge-service-7659dbb6f8-4jvjd 1/1 Running 0 7m7s friend-db-0 1/1 Running 0 7m5s friend-service-559bdfbb99-7f65d 1/1 Running 0 7m7s kafka-0 1/1 Running 1 7m5s kafka-1 1/1 Running 0 4m29s kafka-2 1/1 Running 0 3m32s recommendation-service-6877bbfc4b-p5nmz 1/1 Running 0 7m6s social-network-grafana-96dbbf87-rwjjv 1/1 Running 0 7m6s social-network-neo4j-core-0 1/1 Running 0 7m5s social-network-prometheus-kube-state-metrics-86c8c74d9-sxbbm 1/1 Running 0 7m6s social-network-prometheus-node-exporter-4v49v 1/1 Running 0 7m7s social-network-prometheus-node-exporter-lbgrp 1/1 Running 0 7m6s social-network-prometheus-node-exporter-z78ld 1/1 Running 0 7m6s social-network-prometheus-server-b8d9d948c-gd456 2/2 Running 0 7m6s social-network-zookeeper-0 1/1 Running 0 7m5s social-network-zookeeper-1 1/1 Running 0 5m47s social-network-zookeeper-2 1/1 Running 0 5m9s user-db-0 1/1 Running 0 7m5s user-service-8988d7db4-kdlgx 1/1 Running 0 7m6s
8. Run the App.
In this sample application edge-service is used as API Gateway (Spring Cloud Gateway) used to access REST APIs exposed by different microservices. You need to do port forwarding using kubectl port-forward command to access the application as shown below.
$ kubectl --namespace social-network port-forward svc/edge-service 9000 Response: ----------- Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9000 -> 9000
You can run the following scripts (generate-parallel.sh & generate-serial.sh) to add test users and friend relationships to the social network. Let’s use genereate-serial.sh script to generate some users and friend relationship data in the database as shown below.
/event-sourcing-microservices-example/deployment/sbin (sneppets-gcp)$ ls
generate-parallel.sh generate-serial.sh names-100.txt names-15.txt
$ sh ./generate-serial.sh
Using edge-service URI: localhost:9000
--> Wake up user service... "UP"
--> Wake up friend service..."UP"
--> Wake up recommendation service..."UP"
====> Create users
{
"firstName": "Andrew",
"lastName": "Rutherford",
"createdAt": "2020-02-25T07:17:25.890+0000",
"lastModified": "2020-02-25T07:17:25.890+0000",
"id": 1
}
{
"firstName": "Andrew",
"lastName": "Parr",
"createdAt": "2020-02-25T07:17:27.184+0000",
"lastModified": "2020-02-25T07:17:27.184+0000",
"id": 2
}
{
"firstName": "Emily",
"lastName": "Morgan",
"createdAt": "2020-02-25T07:17:27.894+0000",
"lastModified": "2020-02-25T07:17:27.894+0000",
"id": 3
}
{
"firstName": "Kevin",
"lastName": "Bailey",
"createdAt": "2020-02-25T07:17:28.590+0000",
"lastModified": "2020-02-25T07:17:28.590+0000",
"id": 4
}
-------------
-------------
-------------
====> Create 100 friendships...
10 ❤ 14
{
"id": 1,
"userId": 10,
"friendId": 14,
"createdAt": "2020-02-25T07:21:18.758+0000",
"updatedAt": "2020-02-25T07:21:18.758+0000"
}
7 ❤ 8
{
"id": 2,
"userId": 7,
"friendId": 8,
"createdAt": "2020-02-25T07:21:20.098+0000",
"updatedAt": "2020-02-25T07:21:20.098+0000"
}
------------
------------
------------
Now, let us test few simple API’s like below that are exposed by the gateway.
Get User
GET http://localhost:9000/user/v1/users/{0}
$ curl http://localhost:9000/user/v1/users/20
Response:
----------
{
"firstName":"Andrew",
"lastName":"Parr",
"createdAt":"2020-02-25T07:22:31.238+0000",
"lastModified":"2020-02-25T07:22:31.238+0000",
"id":20
}
Find Friends
GET http://localhost:9000/friend/v1/users/{0}/friends
$ curl http://localhost:9000/friend/v1/users/20/
Response:
---------
[
{
"id":6,
"userId":20,
"friendId":19,
"createdAt":"2020-02-25T07:22:39.969+0000",
"updatedAt":"2020-02-25T07:22:39.969+0000"
}
]
Congratulations, you had successfully deployed the distributed system on Google Cloud and could generate some sample data and test few REST API’s.
9. Metrics and Monitoring
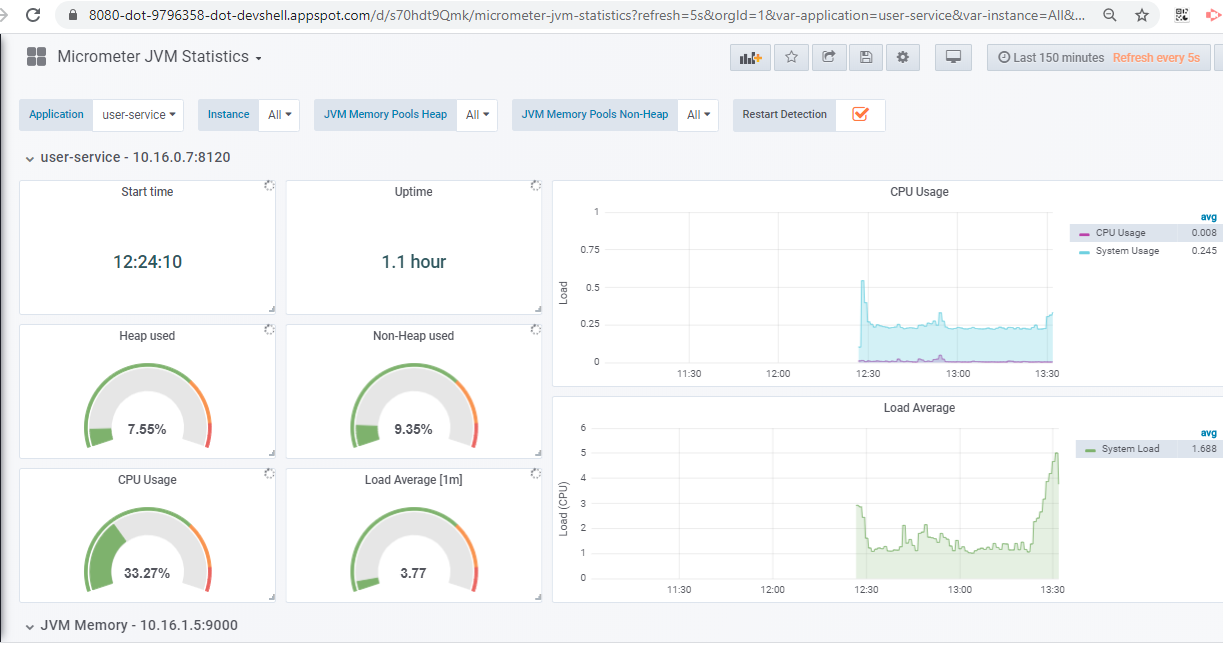
Run the following command to access grafana for visualizing the aggregated metrics. Note, metrics of each microservices application are forwarded to a prometheus gateway, which is responsible for aggregating all the metrics.
$ gcloud container clusters get-credentials social-network-cluster --zone us-central1-a --project sneppets-gcp \
> && kubectl port-forward --namespace social-network $(kubectl get pod --namespace social-network \
> --selector="app=grafana,release=social-network" --output jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') 8080:3000
Response:
----------
Fetching cluster endpoint and auth data.
kubeconfig entry generated for social-network-cluster.
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 3000
Handling connection for 8080
Now, you can access Grafana via browser using “Open in web preview” option in Google Cloud Platform Dashboard/Console and enter the following credentials (username: admin, password: password) to login.
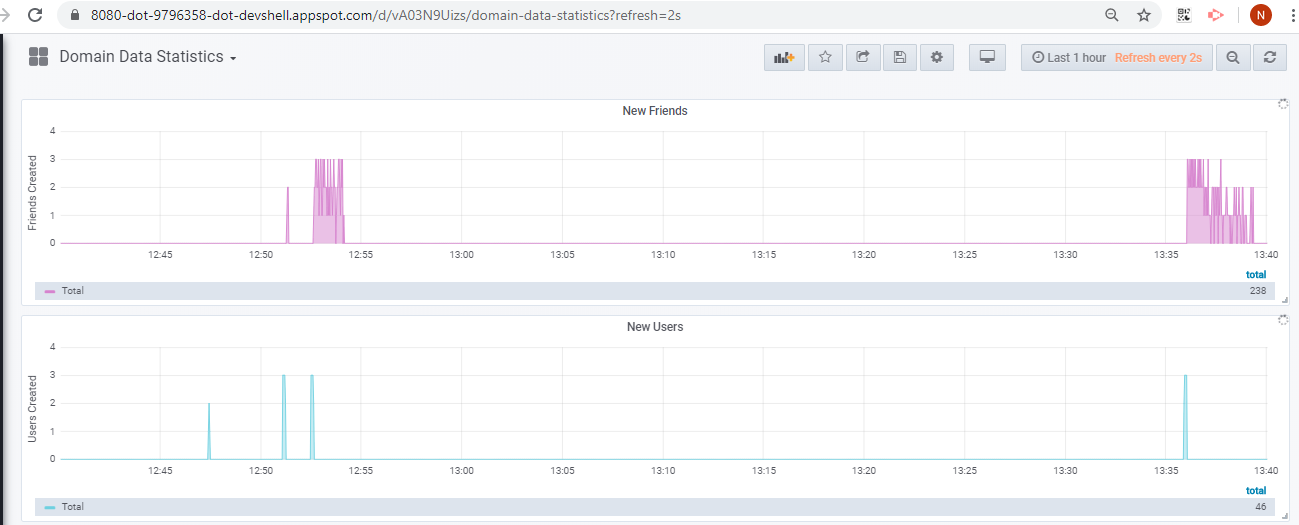
You can also navigate to “Domain Data Statistics” to check how the cluster is able to handle the requests for creating new users and new friends.
10. Clean Up
You need to run the following commands to uninstall the applications (services)
$ helm delete --purge social-network Response: --------- release "social-network" deleted $ kubectl delete pvc datadir-social-network-neo4j-core-0 -n social-network Response: --------- persistentvolumeclaim "datadir-social-network-neo4j-core-0" deleted
Finally, delete the kubernetes cluster that you have created from Google Cloud Platform Console.
Also See:
- Visualize Big Data using Google Data Studio.
- Google Compute Engine Introduction and Features
- How to create GCP project on Google Cloud Platform ?
- Kubernetes Error : did you specify the right host or port ?