How to change Jupyter Notebook working directory ?
This tutorial guides you on how to change Jupyter Notebook working directory. Let’s see two ways using which you can change Jupyter Notebook working directory.
Change Jupyter Notebook working directory – Command line
To change working directory via command prompt, you need to follow the below steps.
1: First, open cmd prompt and run the following jupyter noteboook command.
> jupyter notebook --generate-config Writing default config to: C:\Users990\.jupyter\jupyter_notebook_config.py
The above command will create a config file called “jupyter_notebook_config.py“.
2: Open the file “jupyter_notebook_config.py” from that location in a file editor.
3: After opening that file in an editor, search for the text “# c.NotebookApp.notebook_dir = ”“
4: Then, uncomment that line and update the required path i.e., new working directory and save the modifications.
For example,
c.NotebookApp.notebook_dir = "C:\Users990\Documents\sneppets\Workspaces\Python\Examples"
5: Finally, run the following command in the command prompt.
> python -m notebook
[I 18:47:19.270 NotebookApp] The port 8888 is already in use, trying another port.
[I 18:47:19.271 NotebookApp] The port 8889 is already in use, trying another port.
[W 18:47:19.278 NotebookApp] Terminals not available (error was No module named 'winpty.cywinpty')
[I 18:47:19.279 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: C:\Users990\Documents\sneppets\Workspaces\Python\Examples
[I 18:47:19.279 NotebookApp] Jupyter Notebook 6.3.0 is running at:
[I 18:47:19.279 NotebookApp] http://localhost:8890/?token=9cb56d43292734fd1587083d37be16b31e57199cd498eb33
[I 18:47:19.281 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8890/?token=9cb56d43292734fd1587083d37be16b31e57199cd498eb33
[I 18:47:19.281 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
[C 18:47:19.328 NotebookApp]
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser:
file:///C:/Users/91990/AppData/Roaming/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-22552-open.html
Or copy and paste one of these URLs:
http://localhost:8890/?token=9cb56d43292734fd1587083d37be16b31e57199cd498eb33
or http://127.0.0.1:8890/?token=9cb56d43292734fd1587083d37be16b31e57199cd498eb33
You could observe log messages like notebooks are being served from local directory : C:\Users\91990\Documents\sneppets\Workspaces\Python\Examples. Yay! the working directory is changed.
Change Working Directory Notebook – Command line Option 2
There is another approach using which you can change Notebook’s working directory from command line itself using the following syntax.
jupyter notebook --notebook-dir = <working_directory>
For example, run the following command.
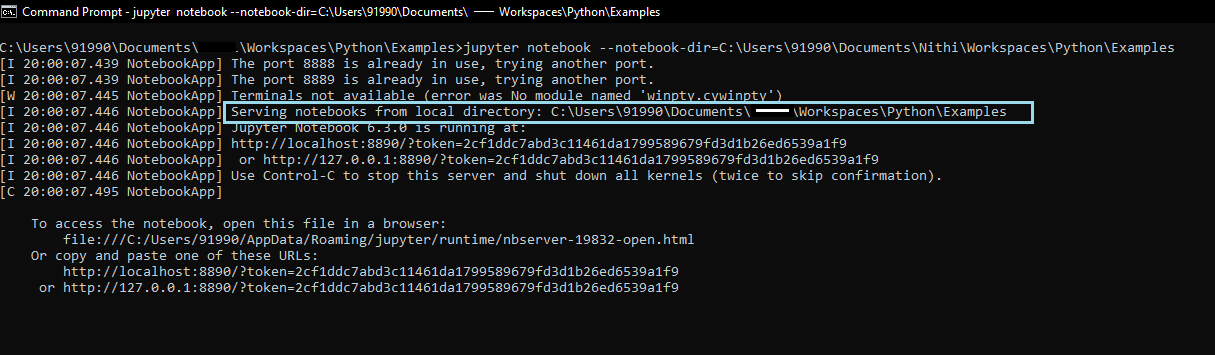
> jupyter notebook --notebook-dir=C:\Users990\Documents\sneppets\Workspaces\Python\Examples
Now the working directory is changed to local directory: C:\Users\91990\Documents\sneppets\Workspaces\Python\Examples.
That’s it. You had learnt how to change Jupyter working directory from the command line in two ways.
Hope it helped 🙂
You’ll also like:
- Increase the cell width of the Jupyter Notebook in browser
- Add python3 kernel to jupyter IPython notebook ?
- Reset jupyter notebook theme to default theme
- How to change the default theme in Jupyter Notebook ?
- Change the Jupyter Notebook startup folder in Windows & Mac
- To run Jupyter Notebook on Windows from command line
- Run a Jupyter Notebook .ipynb file from terminal or cmd prompt
- Amazon Linux AMI : apt-get command not found
- Linux: sudo: apt-get: command not found
- How to Start Stop Restart MariaDB on Linux OS ?
- Putty Fatal Error No supported authentication methods available
- Find which users belongs to a specific group in linux
- How to unzip a zip file from Terminal (Google Cloud Shell)
- What is %matplotlib inline and how to use ?
- Is it possible to change Google Cloud Platform Project ID ?
- Embed image in jupyter notebook from a local file or web resource
- Install Python 3 on Windows 10 machine
- Can I use multiple values.yaml files for Helm Chart ?
- TypeError: a bytes-like object is required, not ‘str’ – Python3